Credit Card Debt in Q3 2023
In 2023, the United States saw significant shifts in credit card debt levels, particularly in Q3. This article examines these changes, placing a spotlight on Q3 2023 and drawing comparisons with earlier quarters.
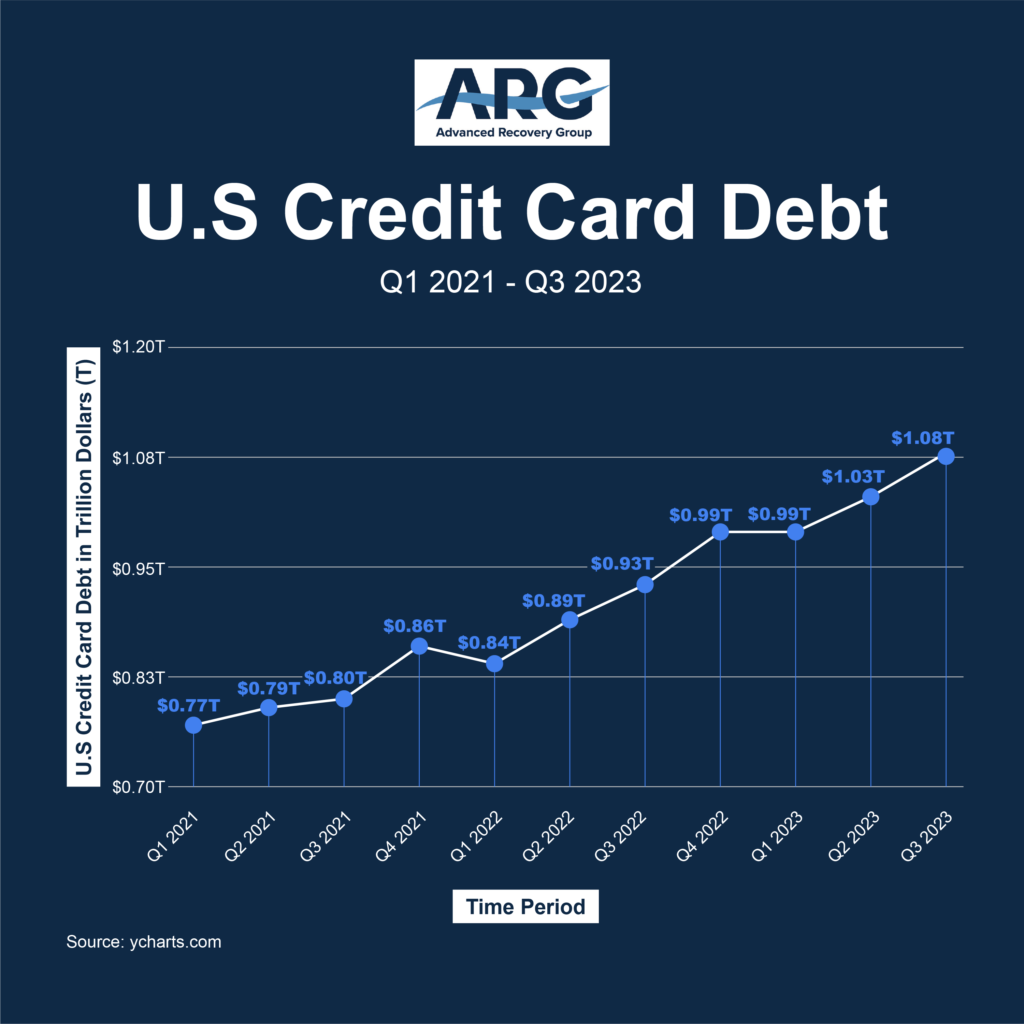
In Q3 2023, U.S. household debt levels, driven largely by credit card borrowings, surged. Overall debt reached $17.29 trillion, with credit card borrowing increasing by 4.7% to $1.08 trillion, as reported by the New York Fed. This increase is the largest since the Fed began tracking such data in 1999. The economic activity during this period was robust, growing at 4.9%, the fastest in two years, despite rising interest rates and borrowing costs. However, alongside this growth, debt delinquency also rose, with the overall flow of debt moving into delinquency increasing compared to the same period last year.
Comparison with Q2 2023
In Q2 2023, total U.S. credit card debt crossed $1 trillion for the first time, reaching $1.03 trillion. This marked a $45 billion rise from Q1 2023, highlighting the significant growth in credit card debt compared to other types of debts like auto loans and mortgages. The average household credit card balance and the average credit card interest rate on overdue payments also showed considerable increases.
Q1 2023 Overview
According to the 2023 American Household Credit Card Debt Report, Q1 2023 saw credit card debt reach $0.99 trillion, a 17.38% increase compared to the previous year. Credit card limits hit an all-time high of $4.51 trillion, and the creation of new credit card accounts rose by 6.7% between 2022 and 2023. Interestingly, credit card delinquency rates, especially among younger age groups, also saw a significant uptick.
Conclusion
The credit card debt landscape in 2023 is marked by rising consumer confidence and increased spending, evidenced by the continual rise in debt levels through each quarter. The surpassing of $1 trillion in Q2 and the continued increase in Q3 point to a robust consumer economy. However, this upward trend also raises concerns about increasing delinquency rates and the financial challenges faced by some borrowers, particularly the younger demographic.
As we look towards the future, particularly into 2024 and beyond, the trajectory of credit card debt in the U.S. remains a topic of considerable interest and speculation. According to the latest data, U.S. credit card debt stands at approximately $1.079 trillion, up from $1.031 trillion in the previous quarter and a significant increase from $0.925 trillion a year ago. This marks a change of 4.66% from the last quarter and an impressive 16.65% from the year before.
The average growth rate of credit card debt in the U.S., currently at 3.48%, offers a baseline for projecting future trends. Looking ahead, several factors will likely influence the direction of credit card debt levels:
- Economic Recovery and Consumer Confidence: As the economy continues to recover from the pandemic, consumer confidence and spending are likely to increase. This may lead to higher credit card usage, potentially increasing overall debt levels.
- Interest Rates and Inflation: The Federal Reserve’s stance on interest rates will be crucial. Higher interest rates can lead to more expensive borrowing costs, which might temper the growth of credit card debt. Conversely, if inflation remains high, consumers may rely more on credit to manage day-to-day expenses, pushing debt levels up.
- Financial Literacy and Credit Management: An increased focus on financial literacy and responsible credit management can influence consumer behavior. More informed consumers might lead to a slower growth in credit card debt, as people become more cautious about accumulating high-interest debt.
- Technological Advancements: Technological innovations in financial services, including more accessible online banking and budgeting tools, may help consumers manage their credit more effectively, potentially influencing credit card debt levels.
- 5Regulatory Changes: Any new regulations relating to credit card companies and consumer lending could impact how credit is extended and managed, thereby affecting overall debt levels.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic factors, such as trade policies, geopolitical events, and international market trends, can indirectly influence U.S. economic health and, by extension, credit card debt levels.
While the exact trajectory of credit card debt into 2024 remains uncertain, these factors will likely play a significant role in shaping the landscape. It will be essential for consumers, policymakers, and financial institutions to stay informed and adapt to these evolving dynamics. We will keep monitoring credit card debt with the next update available after Q4 2023.